In collaboration with leading builder Emaar, Hitachi has reclaimed waste water to keep the magnificent Dubai Fountain running for years to come.
The Dubai Fountain, built by Emaar, is located in the heart of the city’s growing downtown core. Each year, millions of visitors watch in awe as towering streams of water shoot up into the air, synchronized to recognizable instrumental tunes played on surrounding speakers.
Emaar, a premier builder within the United Arab Emirates, has created a fountain consisting of five circles that are joined by two curving lines stretching over 900 feet in length. This is the world’s tallest performing water fountain, and is positioned inside the 30-acre Burj Lake.
Each day, hundreds of liters of water are lost to evaporation in the desert heat. To replenish this water loss, Hitachi has built a system to reuse water from the neighboring Burj Khalifa and downtown sector.

The challenge was to create a sustainable system that was both cost and energy efficient by using available resources. Hitachi’s team looked to reclaim sewage water generated by the adjoining Burj Khalifa and downtown area. This idea created its own set of problems. Hitachi had to ensure the water was free of any unsafe toxins, as fountain water could come in contact with the viewing public in high-wind conditions. Further, water used in the fountain’s musical performance could not have any detectable smells that would deter audience attendance.
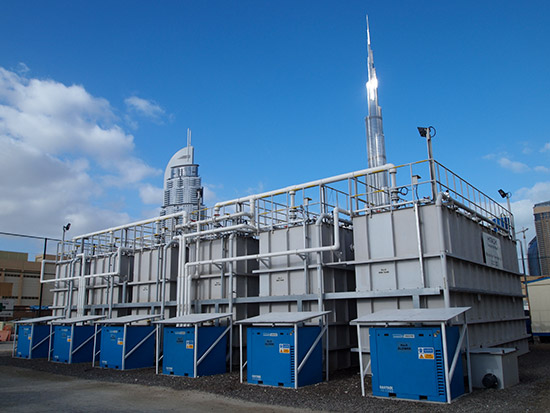

Collecting sewage water from the nearby Burj Khalifa and downtown core, Hitachi constructed a system around the Membrane Bio-Reactor (MBR) units and Reverse Osmosis (RO). These technologies have been developed by Hitachi over many years of working in the field of waste water treatment. The designed solution cleans 2000 cubic meters of sewage water daily.
The sewage water is processed in stages. First it passes through multiple screens that remove grit, grease and sediment, freeing the water of heavy solids. Water is then sent to an intermediate tank before it is forced through a fine screen that expels any particles larger than 1 to 2 millimeters in diameter. After screening, the water is aerated and oxidized to eliminate microorganisms. During aeration, the water passes through the MBR units.
The MBR units process the water through a membrane with a pore size of 0.1 micron. This micro-filtration system not only removes suspended solids, but also bacteria such as coliform. Water is then dosed with disinfectant NaOCI (sodium hypochlorite), which eradicates any residual traces of smell. Upon completion of this stage, the water is pumped into one of two holding tanks. From the holding tanks, and before it is released to the fountain, the water undergoes reverse osmosis. This process ensures the water’s purity and discharges any dissolved contaminants.
Reverse osmosis works by sending pressurized water through a semi-permeable membrane that allows only fresh water through. Reverse osmosis is an extreme treatment that completely removes dissolved solids. After reverse osmosis processing, the water is safe to drink. This is done to safeguard the public, as mist from the powerful jets can fall on the adoring crowds during windy conditions. Additionally, the process removes any salt crystals that may be present. Over time, salt residue would build in the nozzle heads if left untreated, diminishing the height and consistency of the intense water jets.
Hitachi’s design has been a great success, as exhibited by thousands of patrons who watch the fountain’s performance every day in wonderment.

Hitachi continues to look for ways to protect and preserve our precious water. The company hopes to build on the initiatives it took in the Dubai Fountain project and use the lessons learned elsewhere.
Currently, Hitachi is integrating unique technologies that improve water treatment solutions and the management of such facilities. We realize it by analyzing digital data to see where energy saving can be incorporated and to optimize performance through pre-detection of defective equipment. These actions are taken in an effort to make Hitachi’s technologies smarter and safer to use.
The desert is a special place where water is a scarce commodity. Hitachi is proud to have built a system that recycles and reuses water instead of letting it go to waste.
Release Date: March, 2018
Solutions By: Hitachi, Ltd., Water Business Unit