Due to a heavy dependency on fossil fuels as energy sources, the State of Hawaii, U.S., has been rushing to integrate large amounts of renewable energy into its utility grid, causing new trouble, such as excess energy and instability in the power supply. Hitachi has been seeking solutions to this challenge through participation in the Japan-U.S. Smart Grid Demonstration Project and through collaborative creation with local partners and volunteers.
There are many island countries, like Japan, in the world. These countries tend to face energy challenges, including a heavy dependency on fossil fuels as energy sources. In the U.S., Hawaii has been the state with the highest rate of dependency on fossil fuels. Including fuel use in vehicles and airplanes, 90% of Hawaii's energy consumption has been reliant on fossil fuels.
To reduce this dependency, the State of Hawaii has been working toward a goal of supplying 100% of the state's energy through renewable sources by 2045. However, as energy output from renewable sources can vary due to changing environmental conditions, integrating large amounts of renewable energy can make the utility grid unstable by creating obstacles such as increased voltage and fluctuations in frequency.
The Japan-U.S. Smart Grid Demonstration Project was launched to address issues that arise with the increased use of renewable energy. In 2011, Hitachi started working on the Japan-U.S. Island Grid Project (commonly referred to as the "JUMPSmartMaui") which is being entrusted to the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) in collaboration with partners including the State of Hawaii, Hawaiian Electric Company, Inc., the University of Hawaii, and three U.S. national laboratories.
JUMPSmartMaui is an effort to demonstrate the world's latest island style smart grid. The project has three objectives: to respond to the growth of EV (electric vehicle) utilization; to stabilize the supply of electricity; and to maximize the use of renewable energy. Hitachi is managing this demonstration project to build a smart grid system.
Hitachi adopted six innovative initiatives in the JUMPSmartMaui project. The first is the efficient use of renewable energy. This was achieved by such measures as using the system to restrict EV charging times in accordance with renewable energy power generation projections. The second is to develop solutions to stabilize and balance power output coming from renewable sources, as the output from these sources is prone to fluctuation. For example, to deal with a sudden cessation of wind, the system takes direct control of appliances in households and of EVs, controlling the usage of electrical power with the intended effect of minimizing the effects on people's daily lives. The four other initiatives are: to develop facilities and systems to respond to growth in EV utilization; to ensure cybersecurity for system safety; to improve energy control using an autonomous decentralized system; and to support community and infrastructure evolution by developing technologies for information and control platforms. Through these initiatives, Hitachi has been working to realize a low-carbon society while improving the quality of life for people on Maui Island.
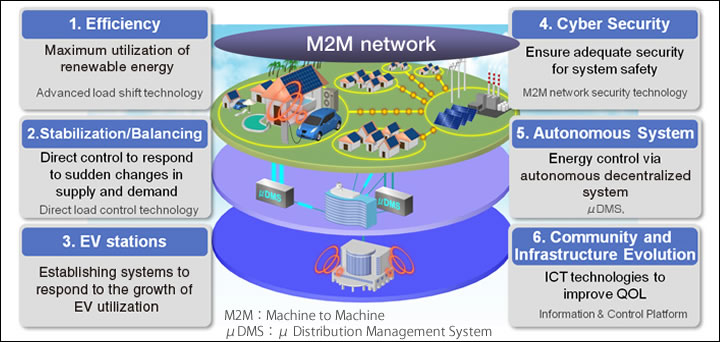
Hitachi's six innovative initiatives
This demonstration project revealed that EVs, which have been gaining in popularity, can play an essential role in developing an efficient smart-grid system. Excess energy being generated can be used to charge batteries in EVs, and the power stored in EV batteries can be used to stabilize the use of electricity from renewable sources. In that way, EVs become an important part of an energy infrastructure that does not overly depend on fossil fuels. Based on this idea, Hitachi set up an energy control center to manage EV charging. In addition, Hitachi set up EV Quick Charger stations, based on an analysis of traffic flow, the location of major destinations, and general convenience for users, and began test demonstrations in December 2013. After linking this system to wind power generation systems in operation on Maui and to the grid, Hitachi has been using IT to carry out the demonstration of an EV operation and charging control system that involves multiple types of quick-charger stations and user-demand response technology. Working closely with local partners and volunteers has been essential in advancing these efforts. During this project, in particular, Hitachi has been demonstrating the value of "Collaborative Creation" to develop new systems.

EV Quick Charger station

Hitachi collaborated with more than 200 volunteers and local stakeholders on the JUMPSmartMaui project.
Hitachi established vehicle-to-grid technology (V2G), which utilizes the electric discharge capability of EVs to feed electricity back into the grid, and also conducted integrated management of these EVs, storage batteries, and other types of dispersed power sources. This resulted in the expansion of VPPs (Virtual Power Plants), a technology that contributes to balancing energy supply and demand throughout the island, into a demonstration system. Also conducted were an analysis and evaluation of the effects of the smart grid, an evaluation of the economics of the configured system, and the building and verification of a business model of a system that realizes a low-carbon society for island regions.
Building upon the success of these projects, Hitachi will continue to develop innovative solutions that combine information and control technology. Hitachi will also keep working to establish systems whose purpose is to enhance the efficient use of constantly growing renewable energy and EVs.
Release Date: February 2018







