Hydropower Potential of India
- 145,000 MW Hydropower Potential at 60% plant load factor(3)
- 85,000 MW Demand Capacity(3)
The video below gives you a glimpse into India’s hydropower potential and Hitachi’s milestone project in hydropower generation. Read the entire article to get a complete picture of this milestone project - India’s first ultra-high voltage direct current (UHVDC) project North-East-Agra transmission link.
As part of its clean energy commitment, India has continued striving to improve and expand its hydropower generation infrastructure and capacity. In 2019, the government decided to grant renewable status to large hydro projects, making them also eligible for various incentives like financial aid, cheaper credit and alike. Previously, hydro projects up to 25 MW capacity were only recognised as renewables. The landmark decision is expected to further amplify hydropower production in India.
Alongside production capability build-up, the government is also actively collaborating with power pioneers such as Hitachi Energy in developing avant-garde and more efficient transmission networks to strengthen the country’s overall power system.
Achieving a milestone in power transmission projects, Hitachi Energy in partnership with Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd., a Government of India Enterprise, delivered India’s first ultra-high voltage direct current (UHVDC) project ±800 KV North-East-Agra transmission link that connects hydropower-rich North-East with the central part of North India, covering a distance of 1,728 km.
With this installation, India has become the world’s first country to come up with a multi-terminal, ultra-high voltage direct current (UHVDC) transmission link, which is also among the world’s largest high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission projects.

Driven by the motto “Power for All”, the government aims to electrify every home across the country. Also being a vibrant economy, India’s energy requirements are massive and ever-growing. As the country marches on to realize its ‘AatmaNirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Make in India’ dreams, energy consumption is bound to rise.
With an overall installed capacity of more than 50 GW, India today has become the world’s fifth-largest hydropower producer3. Apart from being clean, renewable and cheap in the long run, hydropower also has unrivalled strengths such as quick start and stop capability, quick ramping and instantaneous load acceptance, which is ideal for meeting peak demand and ensuring grid stability. Since India’s national power transmission network is today a single grid operation, grid stability is now more important than ever.
Furthermore, with enhanced production, the need for high voltage networks that enable long-distance, large-volume nationwide transmission with greater efficiency is also being felt. Thankfully, the government has been making significant efforts in this direction. Back in 2003, the Government of India had launched the 50,000 MW Hydroelectric Initiative launched to foster the development of the 65,000 MW hydro potential of Northeast India.
The initiative also paved the way for ground-breaking projects such as North-East-Agra UHVDC transmission superhighway that has revolutionized India’s power transmission landscape with its marquee infrastructure and technology deployment to help minimize the losses associated with bulk power transmission over long distances.
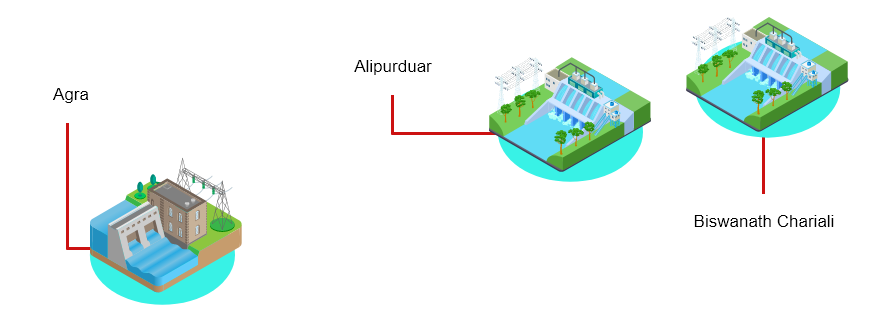
Strategically spread across Biswanath Chariali in Assam, Alipurduar in West Bengal and Agra in Uttar Pradesh, three high capacity converter or transformer stations form the backbone of this project. The state-of-art HVDC converter stations are a joint effort of Hitachi Energy and the state-owned Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL). From system design and development to supply and setting up, both entities played their part.
Importantly, the supply line was to pass through so-called “chicken neck area”, an extremely narrow patch of land (22 km width and 18 km length) near Siliguri in West Bengal – the area is also locked between international borders of Nepal and Bangladesh. Hitachi Energy’ HVDC technology provided an excellent solution to this issue as it used only about one-third of the land as compared to high voltage alternate current (HVAC) technology.
At full capacity, the North-East Agra link will be able to supply enough electricity to serve 90 million people (based on the average national consumption), helping to improve their living standards.
India is making tremendous progress on clean energy, with the government confident of having around 60% of its installed electricity generation capacity from clean sources by 20304. Exceeding the 450 GW target, the renewable energy capacity could touch 510 GW by 2030, including 60 GW of hydro-electric power4. As co-partners to India’s sustainable development, Hitachi through its Social Innovation Business solution is actively collaborating with various stakeholders, including the government, to co-create Social, Economic and Environmental values and help improve people’s Quality of Life.
Utilizing its decades-long OT and IT expertise, Hitachi is passionately working to help India achieve its renewable energy objectives in line with its “Power for All” vision. Through landmark projects like North-East-Agra UHVDC transmission superhighway, Hitachi is also powering good by delivering reliable and clean power supply to millions of people that will not only spur their socio-economic growth but also help build decarbonized and more sustainable society.
1. https://powermin.nic.in/en/content/faqs-hydropower
2. https://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/power/india-to-have-70000-mw-of-hydropower-capacity-by-2030-official/75859241
3. https://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/power/india-overtakes-japan-with-fifth-largest-hydropower-capacity-in-the-world/76095023#:~:text=New%20Delhi%3A%20India%20has%20overtaken,International%20Hydropower%20Association%20(IHA).
4. https://www.financialexpress.com/industry/india-to-have-60-renewable-energy-by-2030-power-minister-rk-singh/2031205/